Dbt Mcp
Official MCP server for dbt (data build tool) providing integration with dbt Core/Cloud CLI, project metadata discovery, model information, and semantic layer querying capabilities.
Docs & Usage Guide
dbt MCP Server
This MCP (Model Context Protocol) server provides tools to interact with dbt. Read this blog to learn more. Add comments or questions to GitHub Issues or join us in the community Slack in the #tools-dbt-mcp channel.
Architecture
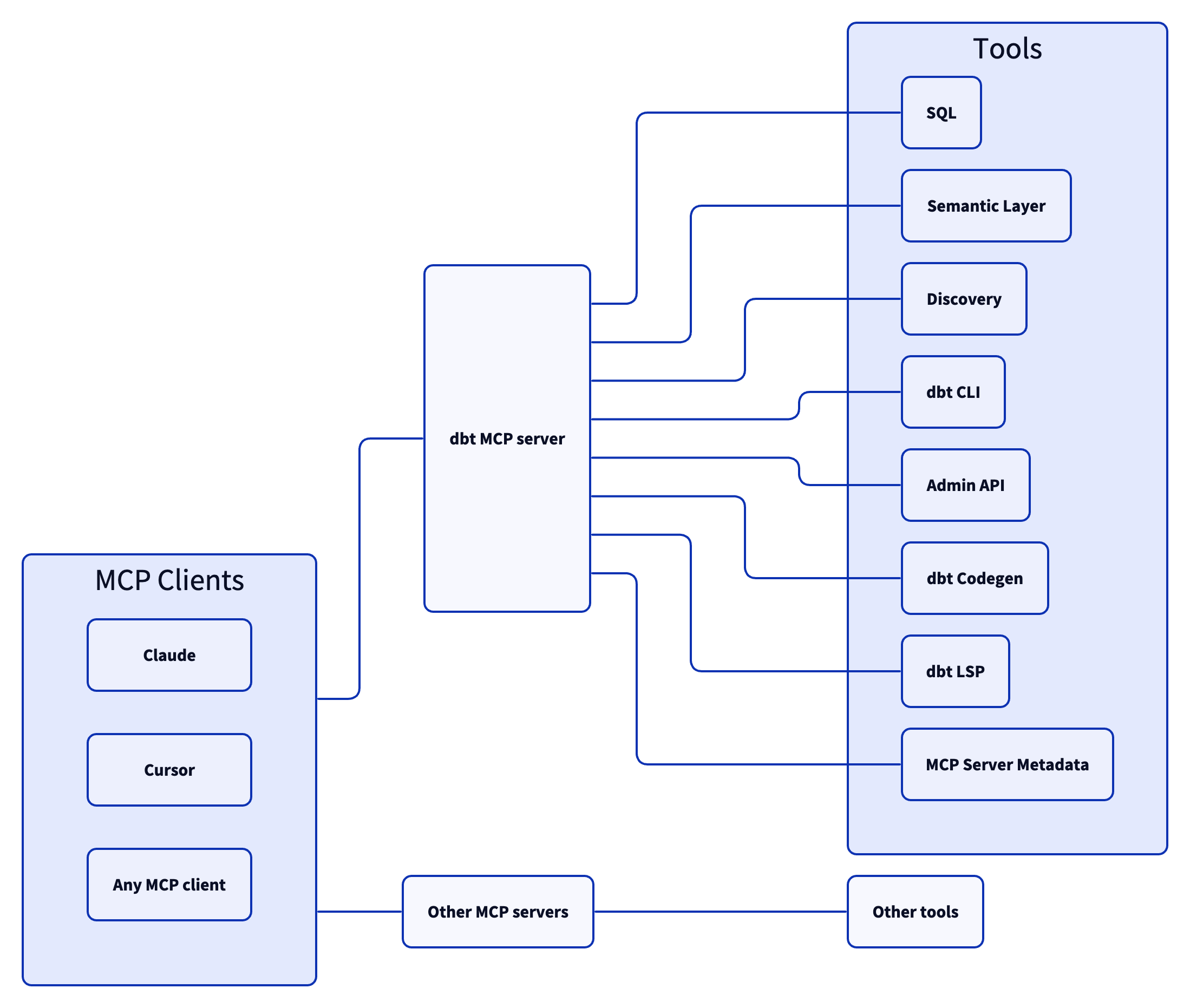
Tools
dbt CLI
build- Executes models, tests, snapshots, and seeds in dependency ordercompile- Generates executable SQL from models, tests, and analyses without running themdocs- Generates documentation for the dbt projectls(list) - Lists resources in the dbt project, such as models and testsparse- Parses and validates the project’s files for syntax correctnessrun- Executes models to materialize them in the databasetest- Runs tests to validate data and model integrityshow- Runs a query against the data warehouse
Allowing your client to utilize dbt commands through this MCP tooling could modify your data models, sources, and warehouse objects. Proceed only if you trust the client and understand the potential impact.
Semantic Layer
list_metrics- Retrieves all defined metricsget_dimensions- Gets dimensions associated with specified metricsget_entities- Gets entities associated with specified metricsquery_metrics- Queries metrics with optional grouping, ordering, filtering, and limiting
Discovery
get_mart_models- Gets all mart modelsget_all_models- Gets all modelsget_model_details- Gets details for a specific modelget_model_parents- Gets parent nodes of a specific modelget_model_children- Gets children models of a specific model
SQL
text_to_sql- Generate SQL from natural language requestsexecute_sql- Execute SQL on dbt Cloud's backend infrastructure with support for Semantic Layer SQL syntax. Note: using a PAT instead of a service token forDBT_TOKENis required for this tool.
Setup
There are two ways to setup dbt MCP, local and remote. Local setup is best for dbt projects that you are developing in a local IDE. Remote setup is better for building custom applications.
Local
- Install uv
- Copy the
.env.examplefile locally under a file called.envand set it with the following environment variable configuration:
Tools
| Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
DISABLE_DBT_CLI |
false |
Set this to true to disable dbt Core, dbt Cloud CLI, and dbt Fusion MCP tools |
DISABLE_SEMANTIC_LAYER |
false |
Set this to true to disable dbt Semantic Layer MCP tools |
DISABLE_DISCOVERY |
false |
Set this to true to disable dbt Discovery API MCP tools |
DISABLE_SQL |
true |
Set this to false to enable SQL MCP tools |
DISABLE_TOOLS |
"" | Set this to a list of tool names delimited by a , to disable certain tools |
Configuration for Discovery, Semantic Layer, and SQL Tools
| Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
DBT_HOST |
cloud.getdbt.com |
Your dbt Cloud instance hostname. This will look like an Access URL found here. If you are using Multi-cell, do not include the ACCOUNT_PREFIX here |
MULTICELL_ACCOUNT_PREFIX |
- | If you are using Multi-cell, set this to your ACCOUNT_PREFIX. If you are not using Multi-cell, do not set this environment variable. You can learn more here |
DBT_TOKEN |
- | Your personal access token or service token. Note: a service token is required when using the Semantic Layer and this service token should have at least Semantic Layer Only, Metadata Only, and Developer permissions. |
DBT_PROD_ENV_ID |
- | Your dbt Cloud production environment ID |
Configuration for SQL Tools
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
DBT_DEV_ENV_ID |
Your dbt Cloud development environment ID |
DBT_USER_ID |
Your dbt Cloud user ID |
Configuration for dbt CLI
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
DBT_PROJECT_DIR |
The path to where the repository of your dbt Project is hosted locally. This should look something like /Users/firstnamelastname/reponame |
DBT_PATH |
The path to your dbt Core, dbt Cloud CLI, or dbt Fusion executable. You can find your dbt executable by running which dbt |
DBT_CLI_TIMEOUT |
Configure the number of seconds before your agent will timeout dbt CLI commands. Defaults to 10 seconds. |
It is also possible to set any environment variable supported by your dbt executable (see here for the ones supported in dbt Core).
We automatically set DBT_WARN_ERROR_OPTIONS='{"error": ["NoNodesForSelectionCriteria"]}' so that the MCP server knows if no node is selected when running a dbt command.
You can overwrite it if needed but we believe that it provides a better experience when calling dbt from the MCP server, making sure that the tool is selecting valid nodes.
Using with MCP Clients
After going through the Setup, you can use dbt-mcp with an MCP client.
Add this configuration to the respective client's config file. Be sure to replace the sections within <>:
{
"mcpServers": {
"dbt-mcp": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": [
"--env-file",
"<path-to-.env-file>",
"dbt-mcp"
]
},
}
}
<path-to-.env-file> is where you saved the .env file from the Setup step
Claude Code
Run the following command to add the MCP server to Claude Code:
claude mcp add dbt -- uvx --env-file <path-to-.env-file> dbt-mcp
By default the MCP server is installed in the "local" scope, meaning that it will be active for Claude Code sessions in the current directory for the user who installed it.
It is also possible to install the MCP server:
- in the "user" scope, to have it installed for all Claude Code sessions, independently of the directory used
- in the "project" scope, to create a config file that can be version controlled so that all developers of the same project can have the MCP server already installed
To install it in the project scope, run the following and and commit the .mcp.json file. Be sure to use an env var file path that is the same for all users.
claude mcp add dbt -s project -- uvx --env-file <path-to-.env-file> dbt-mcp
More info on scopes here
Claude Desktop
Follow these instructions to create the claude_desktop_config.json file and connect.
For debugging, you can find the Claude Desktop logs at ~/Library/Logs/Claude for Mac or %APPDATA%\Claude\logs for Windows.
Cursor
Note the configuration options here and input your selections with this link:
Cursor MCP docs here for reference
VS Code
-
Open the Settings menu (Command + Comma) and select the correct tab atop the page for your use case
Workspace- configures the server in the context of your workspaceUser- configures the server in the context of your user- Note for WSL users: If you're using VS Code with WSL, you'll need to configure WSL-specific settings. Run the Preferences: Open Remote Settings command from the Command Palette (F1) or select the Remote tab in the Settings editor. Local User settings are reused in WSL but can be overridden with WSL-specific settings. Configuring MCP servers in the local User settings will not work properly in a WSL environment.
-
Select Features → Chat
-
Ensure that "Mcp" is
Enabled
-
Open the command palette
Control/Command + Shift + P, and select either "MCP: Open Workspace Folder MCP Configuration" or "MCP: Open User Configuration" depending on whether you want to install the MCP server for this workspace or for all workspaces for the user -
Add your server configuration (
dbt) to the providedmcp.jsonfile as one of the servers:
{
"servers": {
"dbt": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": [
"--env-file",
"<path-to-.env-file>",
"dbt-mcp"
]
}
}
}
<path-to-.env-file> is where you saved the .env file from the Setup step
- You can start, stop, and configure your MCP servers by:
- Running the
MCP: List Serverscommand from the Command Palette (Control/Command + Shift + P) and selecting the server - Utlizing the keywords inline within the
mcp.jsonfile
VS Code MCP docs here for reference
Remote
The remote setup doesn't require running dbt MCP locally. Instead, an HTTP connection is made to dbt MCP running within dbt Cloud. Currently, only Semantic Layer & Discovery tools are supported. To get started, ensure that you have AI Features turned on, and get the following information:
- dbt Cloud host: Use this to form the full URL. For example, replace
<host>here:https://<host>/api/ai/v1/mcp/. It may look like:https://cloud.getdbt.com/api/ai/v1/mcp/. - Production environment ID: This can be found on the
Orchestrationpage of dbt Cloud. Use this to set ax-dbt-prod-environment-idheader. - Service token: To fully utilize Remote MCP, this needs to be configured for the dbt Semantic Layer by following this guide and have
Developerpermissions. Add this as aAuthorizationheader with a value like:token <token>. Be sure to replace<token>with the value of your token.
Then you can use these values to connect to the remote server with Streamable HTTP MCP transport. Use the example here as a reference in Python. A similar implementation is possible with SDKs for many other languages.
You can also connect from MCP clients which support remote MCP with headers. For instance, you can connect Cursor to the remote server with the following configuration. Be sure to replace <host>, <token>, and <prod-id> with your information:
{
"mcpServers": {
"dbt": {
"url": "https://<host>/api/ai/v1/mcp/",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "token <token>",
"x-dbt-prod-environment-id": "<prod-id>",
}
}
}
}
Troubleshooting
- Some MCP clients may be unable to find
uvxfrom the JSON config. If this happens, try finding the full path touvxwithwhich uvxon Unix systems and placing this full path in the JSON. For instance:"command": "/the/full/path/to/uvx".
Contributing
Read CONTRIBUTING.md for instructions on how to get involved!